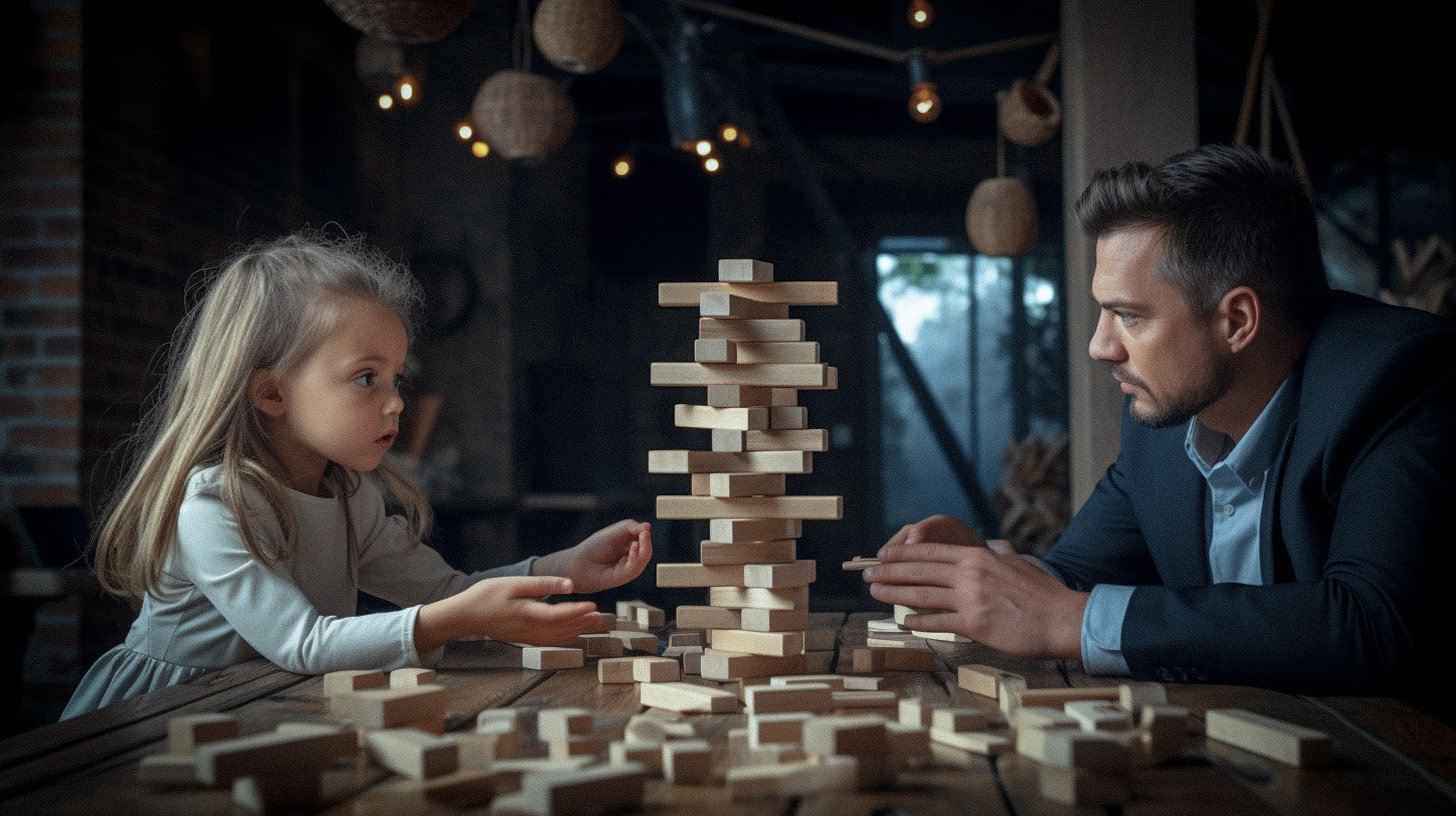
The "Dynamic Industry Structure" is the first of nine components of the Adaptive Competitive Intelligence Model. This concept builds upon Michael Porter's Five Forces Model, which has long been recognized as a powerful tool for understanding the competitive forces that shape an industry.
-
Introduction to Dynamic Industry Structure
-
Analyzing Industry Shifts and Trends
-
Categorizing Industry Change Drivers
-
Case Studies of Dynamic Industry Structures
Intro: Dynamic Industry Structure
Ever played Jenga with a five-year-old? You'll know then, how quickly stable structures can topple! The Dynamic Industry Structure builds upon Michael Porter's Five Forces Model to go beyond the traditional view, accounting for the rapid and often unpredictable changes that characterize today's business environment. It constantly evolves due to influences like technological innovation, market shifts, and regulatory changes.
I. Analyzing Industry Shifts and Trends (the IMPACT Model)
To navigate the ever-changing landscape, businesses need to be adept at analyzing shifts and trends. The IMPACT model consists of the following components that together provide a comprehensive understanding of how industries evolve.
- Innovation Dynamics:
This would cover technological shifts, research and development, and the emergence of new business models. A detailed mapping of innovation trends in the industry could be presented, including diffusion of innovation and the potential impact of emerging technologies.
Example - Innovation Dynamics depicted through a timeline, tracing the trajectory of technological advancements in the industry. - Market Movements:
Here, you can discuss shifts in demand and supply, emerging markets, shifts in consumer behavior, and the influence of digital channels and platforms.
Example — Market Movements represented using demand-supply graphs, market share pie charts, and trend lines for digital proliferation. - Political and Regulatory Changes:
This component would still consider governmental impacts on industry, such as changes in regulation, trade policies, and political stability.
Example — Political and Regulatory Changes mapped out, showing key regulations and their impact. - Adaptability Challenges: This covers how well businesses within the industry are adapting to change, how change is affecting industry structure, and the overall speed of transformation within the industry.
Example — Adaptability Challenges visualized using a scatter plot where companies in the industry are plotted based on their adaptability score. - Competitive Landscape:
Analyze the intensity of competition, new entrants, M&A activity, and competitive strategies being deployed within the industry.
Example — The Competitive Landscape depicted using a competitive forces diagram or competitive positioning map. - Transnational Effects:
This component acknowledges the interconnected nature of modern economies, examining influences such as international trade disputes, global economic trends, environmental considerations, and other cross-border impacts that could affect the industry.
Example — Transnational Effects represented through a global heatmap showing areas of high activity, disruption, or opportunity.
The IMPACT analysis gives a comprehensive understanding of the dynamic industry structure.
Note* each component could be visualized using different diagrammatic tools depending on the depth of analysis required.
Categorizing Industry Change Drivers
Identifying and monitoring the key drivers of change in an industry is essential. These include factors such as technological innovations, governmental policies, economic conditions, and societal trends, each with a distinct impact on the industry.
Case Studies
Learning from real-world examples is an effective way to understand the concept of dynamic industry structures. Later we will delve into case studies of industries that have undergone significant transformations, exploring the catalysts of change, the impact on industry structure, and the lessons that can be drawn for future scenarios.
PREVIOUS: ACIM, the Framework